- About us
- Outsourcing
- Strategic Finance
- Compliance & Tax
- Automation
- Group Companies
- Resources
- Career

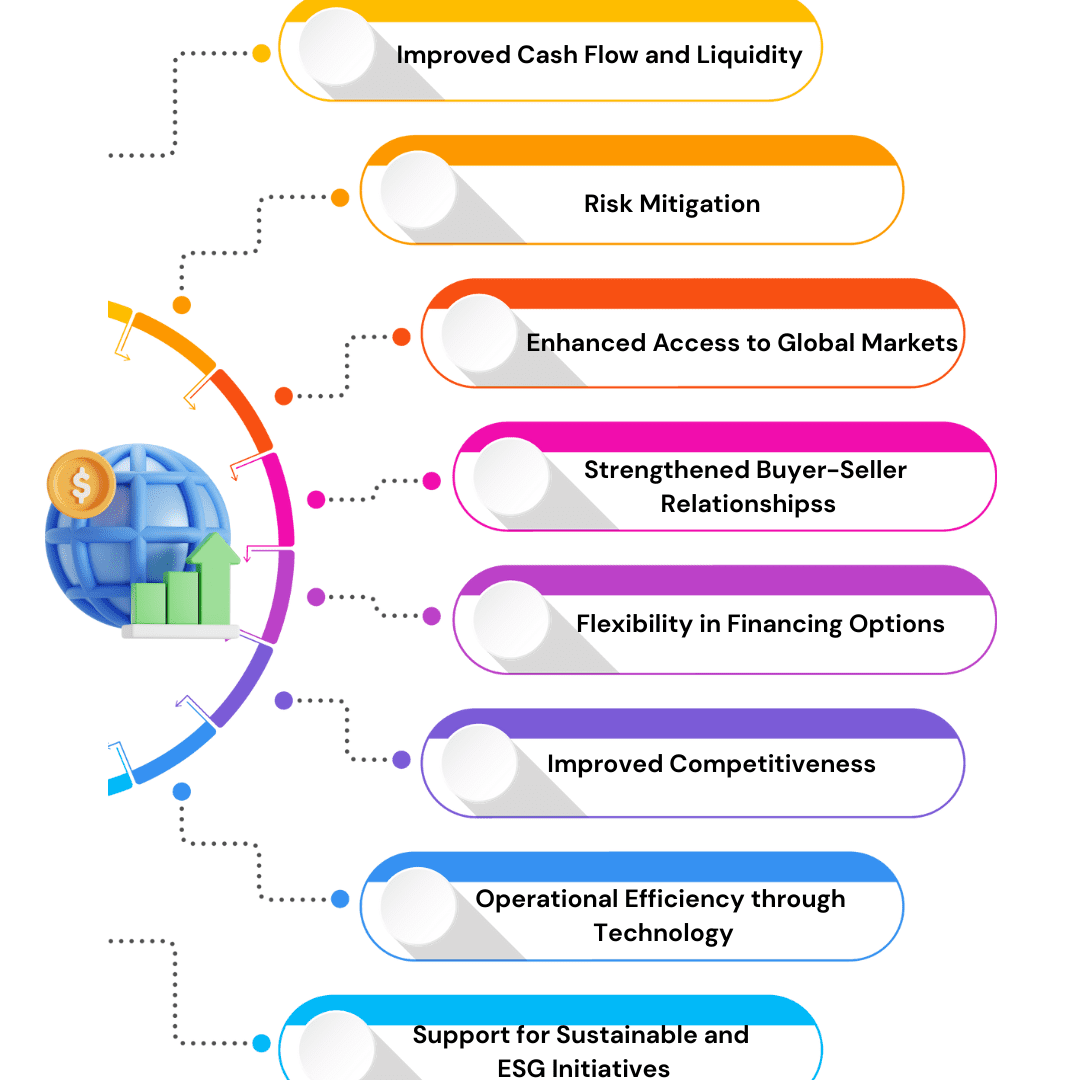
In the complex world of international business, trade finance plays a crucial role in enabling companies to grow while mitigating risks. As businesses expand across borders, understanding the competitive landscape in trade finance becomes essential. This analysis not only helps companies make informed financial decisions but also provides insight into how top competitors structure their services to support global trade.
Trade finance acts as the backbone of global commerce, bridging the gap between exporters and importers by providing the necessary funding, guarantees, and risk management solutions. Without it, businesses may struggle with delayed payments, currency fluctuations, and regulatory hurdles, which can hinder growth and disrupt supply chains.
Moreover, the rapid pace of globalization, coupled with technological innovation, has transformed trade finance into a sophisticated ecosystem of tools and solutions. From letters of credit and invoice financing to pre-shipment and post-shipment funding, companies now have access to a range of instruments that ensure smooth, secure, and timely transactions.
At its core, trade finance is a set of financial instruments and products that help companies conduct international trade efficiently. Whether it’s export finance, invoice financing, or letter of credit, trade finance ensures that both buyers and sellers have the security and liquidity needed to complete transactions.
But why is this important for businesses? Imagine a company exporting goods to multiple countries. Without trade finance solutions, managing payment risks, navigating regulatory requirements, and ensuring timely deliveries becomes challenging. By leveraging trade finance, businesses can maintain smoother cash flows, reduce the risk of defaults, and stay competitive in the global market.
Trade finance is not a single service; it covers multiple areas. Some of the most critical components include:
Ensuring businesses have sufficient short-term funding to meet operational needs without disrupting cash flow. Solutions such as export factoring and domestic factoring help companies convert invoices into immediate cash, improving liquidity and maintaining smooth operations.
Funding support provided before or after goods are shipped. Pre-shipment finance assists exporters in covering production and raw material costs, while post-shipment finance helps maintain liquidity until payments are received. Services like supplier chain financing and distributor channel financing strengthen supply networks by ensuring continuous cash flow across stakeholders.
Credit facilities that provide financial flexibility to both buyers and sellers. Buyer’s credit allows importers to access extended payment terms, while supplier’s credit ensures sellers receive timely funds. Integrated offerings like trade loans and channel financing further enhance trust and efficiency in global trade transactions.
Protection against non-payment risks from international buyers, which is vital when entering emerging or volatile markets. Export credit insurance and advance payment guarantees safeguard businesses from defaults, political risks, or currency fluctuations, ensuring secure international trade.
Beyond traditional trade finance tools, businesses also benefit from:
These areas are interrelated, and companies offering trade finance solutions often combine several products to provide a comprehensive package.
Banks and financial institutions act as intermediaries in international trade, reducing risk, providing liquidity, and ensuring compliance with global trade regulations. Reliable partners can prevent delays and costly transaction issues.
By combining financing, risk management, and technology-enabled services, banks and financial institutions remain indispensable partners in facilitating smooth and secure global trade.
Trade finance is inherently risky, with challenges ranging from currency fluctuations to political instability and shifting regulatory environments. Companies engaged in international trade often face risks such as delayed payments, fraud, insolvency of trading partners, and logistical disruptions due to transportation issues or geopolitical events. Additionally, differences in legal systems, trade policies, and documentation standards across countries can complicate transactions and increase the potential for disputes.
To navigate these risks effectively, leading trade finance providers implement comprehensive risk mitigation strategies, such as:
Ensures compliance with contract terms by controlling the release of shipping documents only when payment or acceptance conditions are met.
Optimizes working capital across multiple stakeholders, enabling suppliers and buyers to maintain liquidity and reduce financial strain.
Protects businesses against buyer non-payment, political risks, and other unforeseen disruptions, giving exporters and importers confidence in cross-border transactions.
Helps mitigate foreign exchange risks that can arise due to currency volatility in international trade.
Advanced analytics and AI-driven tools are increasingly used to identify potential defaults, fraud, or logistical bottlenecks before they impact business operations.
By combining these measures, companies can minimize exposure to financial losses and maintain smoother operations, even in a volatile global trading environment.
Trade finance is evolving rapidly, driven by globalization, technological innovation, and changing business needs. Understanding these trends helps businesses optimize operations, reduce risk, and improve access to capital. Here are the key trends and tools shaping the future of trade finance:
Automated platforms allow businesses to manage transactions, documentation, and compliance in real time.
Features include digital letters of credit, invoice financing, and payment tracking.
Benefits: faster processing, reduced errors, and increased transparency
Artificial intelligence helps analyze credit risks, detect fraud, and forecast cash flows.
Predictive analytics can optimize working capital management and identify potential payment defaults before they occur.
Benefits: smarter decision-making and reduced financial exposure.
Blockchain ensures secure, immutable records for trade transactions.
Smart contracts automate payment release when predefined conditions are met.
Benefits: faster cross-border transactions, lower fraud risk, and higher trust among trading partners.
Companies can finance their suppliers and buyers seamlessly through integrated platforms.
Solutions like pre-shipment finance, post-shipment finance, and export factoring support cash flow across the supply chain.
Benefits: improved liquidity and stronger supplier relationships.
Financial institutions are linking trade finance products to sustainability goals.
Green trade finance products encourage businesses to adopt environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
Benefits: access to specialized financing, improved brand reputation, and compliance with ESG regulations.
Businesses can safeguard transactions through export credit insurance, advance payment guarantees, and currency hedging.
Risk assessment models are increasingly using AI and scenario analysis to minimize exposure.
Benefits: protection against political, commercial, and financial risks in global trade.
More platforms are offering tailored solutions for small and medium enterprises.
Tools include buyer’s credit, supplier’s credit, and faster approvals for trade loans.
Benefits: SMEs gain access to global markets and can compete effectively with larger enterprises.
Faster payment solutions are emerging to reduce transaction times in international trade.
Integration with multiple banks and payment networks enables seamless currency exchange and settlements.
Benefits: improved cash flow and operational efficiency for exporters and importers.
Cloud platforms enable remote access to trade finance tools and dashboards.
Businesses can manage documentation, track shipments, and collaborate with partners globally.
Benefits: scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced operational flexibility.
Partnerships between banks, fintech’s, and logistics providers create integrated trade networks.
These ecosystems allow end-to-end management of trade transactions, from financing to delivery.
Benefits: reduced operational complexity, faster transaction cycles, and increased transparency.
To stay ahead in the competitive trade finance market, benchmarking is essential. This involves analyzing top providers’ products, processes, and strategies to identify gaps and opportunities. Key benchmarking areas include:
Leading competitors offer a mix of pre-shipment finance, post-shipment finance, buyer’s credit, and supplier’s credit. Companies that diversify their offerings can cater to a broader client base, from SMEs to multinational corporations, enhancing market reach.
Top providers mitigate risks through export credit insurance, documentary letter of credit, and advance payment guarantees. Benchmarking risk management practices helps businesses understand how to reduce exposure to defaults, fraud, or currency fluctuations.
Competitors using global trade finance platforms, AI-driven risk analytics, and blockchain-based document verification achieve faster transaction times and higher client satisfaction. Understanding how these tools improve efficiency can guide internal technology investments.
Providers that focus on seamless client experiences, easy application processes, real-time transaction tracking, and customized financing solutions set the standard for client retention. Benchmarking customer service strategies can help businesses enhance loyalty and attract new clients.
Businesses looking to leverage trade finance effectively should focus on actionable strategies that align with competitor insights:
Efficient working capital management is vital for international trade. Companies should use tools like invoice financing, trade loans, and export factoring to ensure liquidity. Proper working capital optimization allows businesses to fulfill orders promptly, negotiate better payment terms, and minimize financing costs.
Understanding export finance and import financing options is crucial. Providers offering buyer’s credit, supplier’s credit, or pre-shipment finance enable companies to manage cash flows efficiently. Exporters can fund production costs, while importers can access goods without immediate capital outlay.
Trade finance inherently involves risk, from political instability to payment defaults. Competitors that excel often integrate export credit insurance, advance payment guarantees, and documentary letters of credit to protect all stakeholders. Businesses should evaluate risk exposure and adopt similar solutions tailored to their trade profiles.
Digital transformation is no longer optional. Platforms that integrate international trade finance with supply chain financing tools reduce transaction delays and errors. AI-based risk assessment and real-time reporting enhance decision-making, allowing businesses to act proactively.
Many competitors focus on SMEs, emerging markets, or specific industries. Companies can explore these untapped opportunities by offering specialized financing solutions, such as export factoring for small exporters or supply chain finance for niche sectors. This approach not only increases revenue streams but also builds long-term client relationships.
The trade finance landscape is rapidly evolving, with several trends influencing how businesses compete and operate:
Increasingly, financiers are linking trade finance solutions to sustainability metrics. Businesses adopting green trade finance or ESG-aligned financing options gain a competitive advantage while meeting regulatory and stakeholder expectations.
Blockchain enhances transparency and reduces fraud in international trade finance. Smart contracts automate payment triggers upon delivery or compliance with contract terms, making transactions faster and more secure.
Partnerships between traditional banks and fintech companies are creating hybrid models. These collaborations allow providers to offer digital trade finance services with faster approvals, seamless documentation, and AI-driven risk analytics.
SMEs are increasingly participating in international trade. Competitors offering export credit, pre-shipment finance, or post-shipment finance solutions specifically tailored for smaller businesses can capture this growing market segment.
Based on competitor analysis and emerging trends, businesses can take the following steps to future-proof their trade finance strategy:
By following these strategies, businesses can not only compete effectively but also innovate in ways that create sustainable growth in the global trade finance market.
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.