- About us
- Outsourcing
- Strategic Finance
- Compliance & Tax
- Automation
- Group Companies
- Resources
- Career
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become one of the most transformative technologies of the digital era automating repetitive tasks, improving accuracy, and helping companies operate faster than ever before. But in 2025 and beyond, RPA is evolving into something even bigger: AI-driven automation, hyper automation, and agentic AI systems that work like digital co-workers.
Whether you are a business owner, manufacturer, IT manager, or simply curious about automation, this guide will help you understand what RPA is, how it works, and why it is becoming essential for modern businesses.
Let’s explore the world of robotic process automation in a simple, humanized, and highly practical way.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to software robots or “bots” that are programmed to mimic the actions a human performs on a computer. These bots follow logical, rule-based steps to complete tasks with speed and accuracy, making them ideal for day-to-day digital operations.
These tasks typically include:
In simple terms, if a task follows a predictable pattern, needs accuracy, and requires hours of manual effort, then RPA can perform it faster, more consistently, and without errors.
Unlike humans, bots don’t get tired, distracted, or overloaded. They work 24/7, complete tasks in seconds, and ensure every step follows the exact rules you’ve set. This makes RPA one of the most reliable technologies for boosting productivity, reducing operational costs, and eliminating human mistakes in everyday workflows.
Real-World Scenario
Imagine an employee manually downloading vendor invoices, checking details, entering them into ERP software, and emailing confirmations. RPA bots can perform this entire workflow automatically saving hours of daily work.
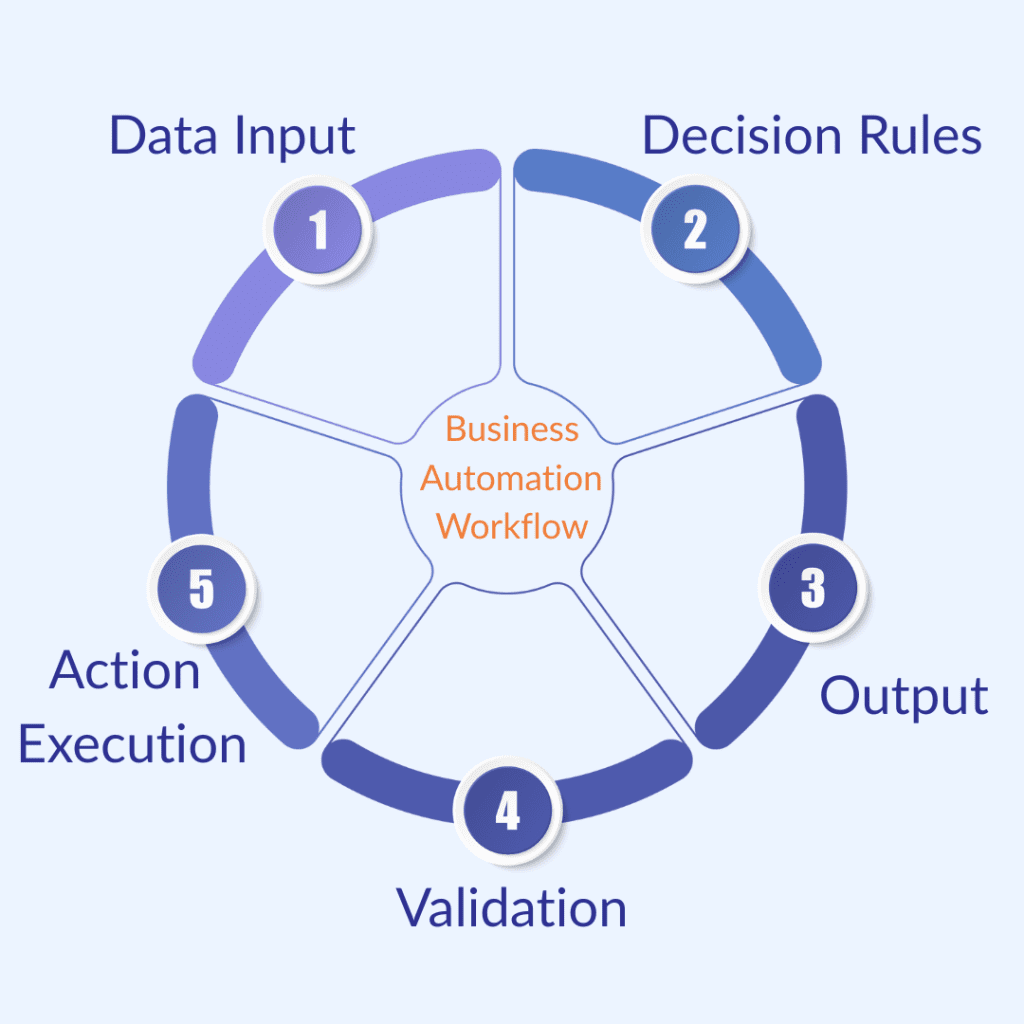
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) may sound complex, but at its core, it follows a very logical step-by-step workflow. Think of it as giving a digital worker clear instructions and the bot executes them perfectly every time. Here’s a closer look at how the process works:
The bot begins by gathering data from multiple sources such as documents, emails, web portals, spreadsheets, or internal databases.
It can:
Once the data is collected, the bot evaluates it using predefined logic.
This includes “if/then” conditions such as:
Next, the bot performs actions across systems such as ERP, CRM, HRMS, banking platforms, or government portals.
It can:
Before completing the process, the bot verifies the data and actions taken.
It checks for:
Finally, the bot generates the required output such as:
RPA isn’t just software; it functions like a dedicated digital employee. It works 24×7, doesn’t make mistakes, and follows every rule exactly as defined. With speed, consistency, and precision, RPA frees human teams from repetitive tasks so they can focus on innovation, strategy, and decision-making.
Example Use Cases
AI-driven automation takes traditional RPA to a whole new level. While standard RPA works best with structured, rule-based tasks, the integration of Artificial Intelligence allows automation to handle far more complex and dynamic processes. With AI, bots can now read and understand unstructured documents using advanced document processing, learn from recurring patterns, and even make decisions based on machine learning models. They can classify invoices, claims, emails, or forms with high accuracy and interact with humans through natural language understanding. This powerful evolution where RPA and AI work together is known as Intelligent Automation, enabling businesses to automate not just repetitive tasks but entire end-to-end workflows that previously required human judgment.
Example
An RPA bot can extract data from a bill.
AI can read if the bill is handwritten, poorly scanned, or differently formatted.
Together, they deliver true end-to-end automation.
Hyper automation represents the next major leap in digital transformation. Unlike traditional automation, which focuses on single tasks, hyper automation integrates multiple advanced technologies to streamline entire business processes from start to finish. It is a powerful blend of RPA, artificial intelligence, process mining, workflow automation, and real-time analytics working together as one unified system. With hyper automation, organizations can automate complex decision-making, uncover inefficiencies, and redesign processes using intelligent insights.
This ecosystem typically includes several tools and capabilities such as RPA for executing repetitive tasks, AI-powered automation for understanding and interpreting data, process mining tools for discovering workflow gaps, and low-code/no-code platforms for building automation quickly without specialized coding skills. It also leverages natural language processing, machine learning models, and enterprise automation software to create a fully connected, self-improving automation environment. In essence, hyper automation enables companies to move beyond simple task automation and achieve end-to-end operational excellence at scale.
Why Hyper automation Matters
It reduces dependency on manual labor and helps companies scale workflows quickly especially useful for industries like banking, insurance, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Earlier, automation required IT teams and developers. Today, platforms such as Automation Anywhere, UiPath, Microsoft Power Automate, and SAP Intelligent RPA allow non-technical teams to create bots easily.
These “citizen developers” can:
Example
A finance executive can build a bot to match invoices with payments without writing a single line of code. This democratization of automation accelerates digital transformation across industries.
Agentic automation refers to AI agents capable of performing multi-step tasks autonomously with reasoning abilities.
Unlike RPA bots, AI agents can:
Where It’s Used?
Agentic systems represent the future of automation blending intelligence with action.
Robotic Process Automation has become a game-changer across industries, delivering speed, accuracy, and cost reduction. Here’s how different sectors benefit from automation:
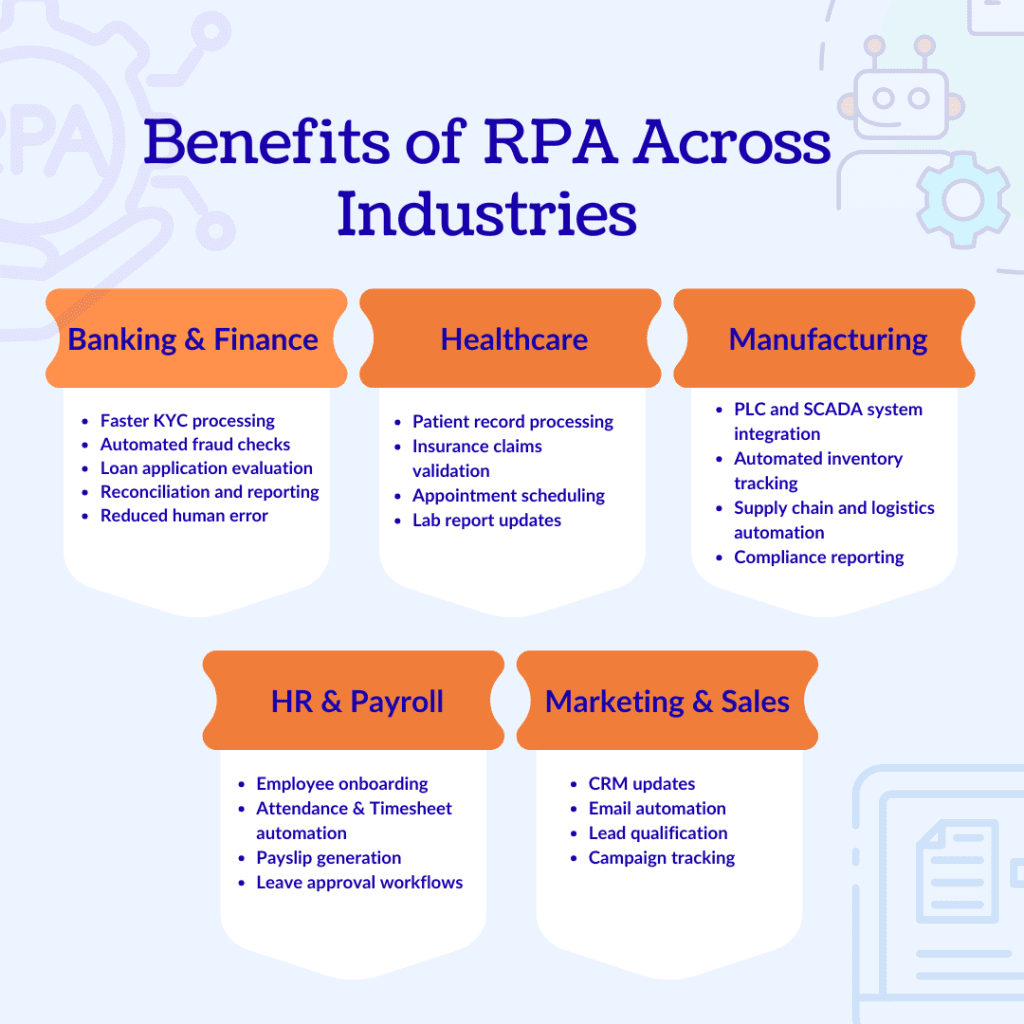
Banking is one of the earliest and largest adopters of RPA because financial workflows involve heavy documentation and high compliance needs. RPA delivers consistent, real-time processing with minimal error.
Key Use Cases:
Faster KYC processing: Bots extract customer data, verify documents, and update systems instantly, reducing onboarding time from days to minutes.
Automated fraud checks: RPA cross-checks transactions, flags anomalies, and supports fraud-risk teams.
Loan application evaluation: Bots validate documents, check credit history, and push data into loan management systems.
Reconciliation and reporting: RPA matches thousands of entries across systems without manual effort.
Reduced human error: By removing manual data entry, accuracy improves and operational costs drop significantly.
Healthcare systems generate massive amounts of patient data every day. RPA helps hospitals, labs, and insurers eliminate administrative overload and focus more on patient care.
Key Use Cases:
Patient record processing: Bots update EHRs and maintain accurate patient histories.
Insurance claims validation: RPA checks eligibility, processes claims, and reduces delays in approvals.
Appointment scheduling: Bots coordinate doctor availability, send reminders, and reduce no-shows.
Lab report updates: Automated entries ensure faster diagnostics and improved communication between departments.
RPA enhances operational efficiency by working alongside systems like PLCs and SCADA. Manufacturers gain visibility, predictability, and smooth workflows.
Key Use Cases:
PLC and SCADA system integration: Bots read system outputs and trigger automated actions or reporting.
Automated inventory tracking: RPA monitors stock levels and updates procurement systems in real time.
Supply chain and logistics automation: Shipment tracking, vendor coordination, and delivery updates become seamless.
Compliance reporting: Bots compile audit-ready reports and reduce the burden of regulatory documentation.
RPA transforms HR teams from manual processors to strategic partners by automating repetitive administrative tasks.
Key Use Cases:
Employee onboarding: Bots create IDs, process documents, and update HRMS systems.
Attendance & timesheet automation: Automated validation ensures error-free payroll cycles.
Payslip generation: RPA pulls data, calculates salary components, and sends payslips automatically.
Leave approval workflows: Bots route requests to managers and update balances without human intervention.
RPA enables revenue teams to focus on strategy and creativity while bots handle the repetitive backend work.
Key Use Cases:
CRM updates: Bots add leads, update notes, and maintain accurate sales pipelines.
Email automation: Automated sequences increase engagement and improve lead nurturing.
Lead qualification: RPA scores leads, validates data, and routes them to sales teams.
Campaign tracking: Bots monitor campaign performance and generate detailed analytics reports.
Across industries whether it’s banking, healthcare, manufacturing, HR, or marketing RPA delivers one consistent advantage:
Lower operational costs
Higher accuracy
Faster processing
Improved customer experience
Boosted productivity
RPA isn’t just a technology upgrade; it’s the foundation of smarter, scalable, and future-ready businesses.
Implementing automation requires planning not just purchasing tools.
Here’s a step-by-step roadmap:
Step 1: Identify Processes to Automate
Ideal processes are:
Examples: invoice processing, payroll, compliance checks.
Step 2: Choose the Right RPA Tool
Popular tools include:
Step 3: Build and Test Bots
Use low-code builders to design workflows and perform pilot testing.
Step 4: Deploy and Monitor
Monitor for accuracy, speed, errors, and ROI.
Step 5: Scale Automation
Integrate with AI, ERP, CRM, and document processing tools.
The RPA lifecycle is a structured roadmap that ensures automation projects are designed, implemented, and scaled successfully. It begins with process discovery, where teams identify repetitive, rule-based tasks that are ideal for automation. Once the right processes are selected, the next step is bot design, which involves mapping workflows, defining business rules, and planning how the bot will interact with systems.
After the design phase, the project moves into development, where RPA developers or citizen developers build the bot using RPA tools. This is followed by the crucial stage of testing, where the bot is validated in a controlled environment to ensure accuracy, stability, and compliance with business logic.
Once the bot clears testing, it enters deployment, becoming an active part of day-to-day operations. But the lifecycle doesn’t end there bots require continuous monitoring to track their performance, handle exceptions, and maintain uptime. Finally, companies engage in optimization, refining bots over time to increase efficiency, add new capabilities, or adapt to changing business processes.
This end-to-end lifecycle ensures that automation remains reliable, scalable, and aligned with organizational goals.
ROI Measurement Includes:
Businesses typically see 40–70% cost savings within the first year.
AI automation is rapidly evolving. The future includes:
RPA is no longer just a tool it is becoming the digital backbone of tomorrow’s intelligent enterprises.
RPA is software that performs repetitive tasks just like a human but faster and without mistakes.
Yes. Most modern platforms support low-code or no-code workflow creation.
No. RPA follows rules, while AI understands patterns and learns. Together, they create intelligent automation.
RPA replaces repetitive tasks not people. Employees can focus on creativity, strategy, and decision-making.
Banking, finance, manufacturing, healthcare, HR, sales, and customer service.
Simple bots can be deployed in days. Complex workflows may take a few weeks.
Yes. Most businesses achieve significant ROI within months.
Robotic Process Automation is no longer a trend it is a fundamental business necessity. With AI-driven automation, hyper automation, and intelligent agents, companies can operate faster, smarter, and more competitively.
RPA reduces repetitive tasks, improves accuracy, and frees employees to focus on meaningful work.
As industries continue to adopt automation, those who embrace RPA early will be better prepared for the future more efficient, more agile, and more innovative.
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.