Exploring the Different Types of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is about managing an organization’s most important asset its people. It includes activities like hiring, training, performance reviews, and managing salaries. The goal of HRM is to create a happy and productive workforce that supports the organization’s goals. HRM plays a vital role in making sure that employees are motivated and working towards the company’s success.
In today’s fast-changing business world, it is important to understand the different types of HRM. Each type offers unique ways to manage people, depending on the organization’s needs and culture. By knowing these different approaches, companies can choose the best HR strategies to keep employees engaged, increase productivity, and stay ahead of the competition.
What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?and Key components of HRM
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a strategic and comprehensive approach to managing an organization’s most valuable asset its people. It encompasses all activities involved in acquiring, developing, motivating, and retaining employees to achieve organizational goals. HRM is not just administrative; it plays a vital role in creating a productive, satisfied, and engaged workforce.

Key components of HRM include:
-
Recruitment & Selection: Attracting and hiring the right talent based on organizational needs.
-
Training & Development: Building employee skills to meet current and future requirements.
-
Performance Management: Evaluating employee performance and providing feedback to enhance productivity.
-
Compensation & Benefits: Offering fair pay, incentives, and perks to motivate employees.
-
Compliance: Ensuring adherence to labor laws, health and safety regulations, and organizational policies.
-
Employee Engagement: Promoting a positive work environment to boost morale and retention.
When is HRM applied in an organization?
HRM is continuous and applies throughout the employee lifecycle from onboarding to retirement. It becomes especially crucial during:
-
Business Expansions or Restructuring
-
Aligns workforce roles with new business strategies.
-
Manages recruitment, training, and integration during mergers or growth.
-
Example: Onboarding employees after a merger and creating a unified company culture.
-
Talent Shortages or Skills Gaps
-
Ensures the right talent is available at the right time.
-
Implements reskilling, upskilling, and targeted hiring programs.
-
Example: Training existing staff in emerging technologies like AI or cloud computing.
-
Implementation of New Technology
-
Supports employees in adapting to new systems or digital tools.
-
Organizes training, guides change management, and ensures productivity.
-
Example: Transitioning to a cloud-based HR system with structured employee onboarding.
-
Organizational Change Initiatives
-
Communicates new policies, procedures, and strategic shifts.
-
Reduces resistance and aligns teams with company goals.
-
Example: Shifting to a remote-first work culture with proper virtual onboarding and engagement programs.
-
Performance Improvement or Productivity Challenges
-
Crisis Management or Workforce Disruption
-
Manages layoffs, remote work, and employee well-being during challenging times.
-
Example: HR programs supporting mental health and flexible work arrangements during a pandemic.
-
Employee Lifecycle Milestones
-
Applies HR practices during onboarding, promotions, career development, and retirement.
-
Example: Structured onboarding programs, leadership succession planning, and retirement benefits management.
How Does HRM Operate in Practice?
HRM operates through structured processes, policies, and strategic planning, covering:
-
Workforce Planning – Forecasting staffing needs and skill requirements.
-
Talent Acquisition – Recruiting candidates who align with the organizational culture and goals.
-
Learning & Development – Conducting training, mentorship, and career development programs.
-
Performance Evaluation – Setting KPIs, reviewing performance, and offering growth guidance.
-
Policy & Compliance Management – Ensuring labor law adherence, maintaining employee records, and managing benefits.
-
Employee Relations – Resolving conflicts, promoting engagement, and maintaining morale.
Tools Used in Modern HRM:
-
HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems)
-
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
-
Payroll & Attendance Automation Tools
-
Performance Management Software
-
HR Analytics Platforms
Classification of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a vital function in every organization, as it focuses on managing the workforce the most important asset for achieving business success. Effective HRM ensures that employees are not only skilled and competent but also motivated, engaged, and aligned with the organization’s goals. To achieve these objectives, HRM is often classified into different types, each tailored to address specific organizational needs, operational challenges, and strategic priorities.
Understanding the different types of HRM is essential because organizations face diverse challenges, depending on their size, industry, culture, and business goals. By recognizing the distinctions between these classifications, companies can implement the most appropriate HR strategies, ensuring efficient management of human capital and sustainable growth. For example, a startup may prioritize operational HRM to establish basic HR functions like recruitment and payroll, while a multinational corporation may focus heavily on strategic HRM to align global workforce planning with long-term business objectives. Similarly, administrative HRM is critical in highly regulated industries, where compliance, record-keeping, and employee benefits management must be meticulously maintained to avoid legal and operational risks.
Types of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) can be broadly classified into three main types: Strategic HRM, Operational HRM, and Administrative HRM. Each type plays a distinct role in managing the workforce effectively, and understanding these distinctions helps organizations implement tailored HR practices that align with their goals, improve productivity, and enhance employee satisfaction.
a) Strategic HRM
Strategic Human Resource Management focuses on aligning human resources with the long-term objectives of the organization. It goes beyond routine HR tasks and emphasizes planning for future workforce needs, developing leadership pipelines, and retaining top talent. Strategic HRM ensures that employee skills, capabilities, and career development initiatives support the company’s overall mission and vision. For example, in a technology company, strategic HRM may involve identifying emerging skill requirements in areas like artificial intelligence or cybersecurity and developing training programs to build this talent internally. By linking HR strategy with organizational goals, strategic HRM helps companies remain competitive, innovative, and agile in a rapidly changing business environment. It also plays a crucial role in fostering a strong corporate culture, encouraging employee engagement, and ensuring that leadership development programs prepare the organization for future challenges.
b) Operational HRM
Operational HRM focuses on the day-to-day management of human resources and ensures that all HR functions run smoothly on a regular basis. This includes recruitment, onboarding, training, performance evaluations, employee relations, and handling workplace issues. Operational HRM ensures that employees are productive, motivated, and supported in their roles. For instance, an operational HR team in a retail organization may oversee scheduling, conduct employee training sessions, monitor attendance, and manage performance reviews to maintain efficiency across stores. By handling these routine activities efficiently, operational HRM allows employees to focus on their core responsibilities and contributes directly to overall organizational performance. It bridges the gap between strategic objectives and daily employee activities, ensuring that the workforce operates cohesively and effectively.
c) Administrative HRM
Administrative HRM is concerned with managing HR processes, maintaining records, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and company policies. It focuses on tasks such as payroll management, benefits administration, maintaining employee records, leave management, and adhering to statutory requirements. Administrative HRM plays a critical role in reducing legal and operational risks while keeping HR functions organized and transparent. For example, in a healthcare organization, administrative HRM ensures accurate payroll processing, timely benefits distribution, and compliance with employment regulations. By efficiently handling these administrative responsibilities, this type of HRM creates a reliable backbone for the organization, enabling operational and strategic HR activities to function without disruption.
What are the Key Areas of HRM?
-
HR Planning & Development
-
Prepares the workforce for future needs.
-
Uses analytics for workforce forecasting.
-
Implements training, mentorship, and succession planning.
-
HR Policies & Compliance
-
Provides workplace rules and governance.
-
Ensures labor law compliance.
-
Uses automation to track records and maintain legal adherence.
-
Training & Development
-
Enhances employee skills and knowledge.
-
Leadership training builds future organizational leaders.
-
HR software supports online learning, tracking, and evaluation.
-
HR Operations & Metrics
-
Manages recruitment, payroll, attendance, and employee engagement.
-
Tracks performance using KPIs like turnover, productivity, and engagement rates.
-
Automation increases efficiency and reduces errors.
-
HR Outsourcing & Consulting
-
Outsourcing reduces costs and provides expertise for small or mid-sized businesses.
-
Consulting supports strategic HR transformation, digitalization, and compliance.
Overview of Key HR Roles and Responsibilities
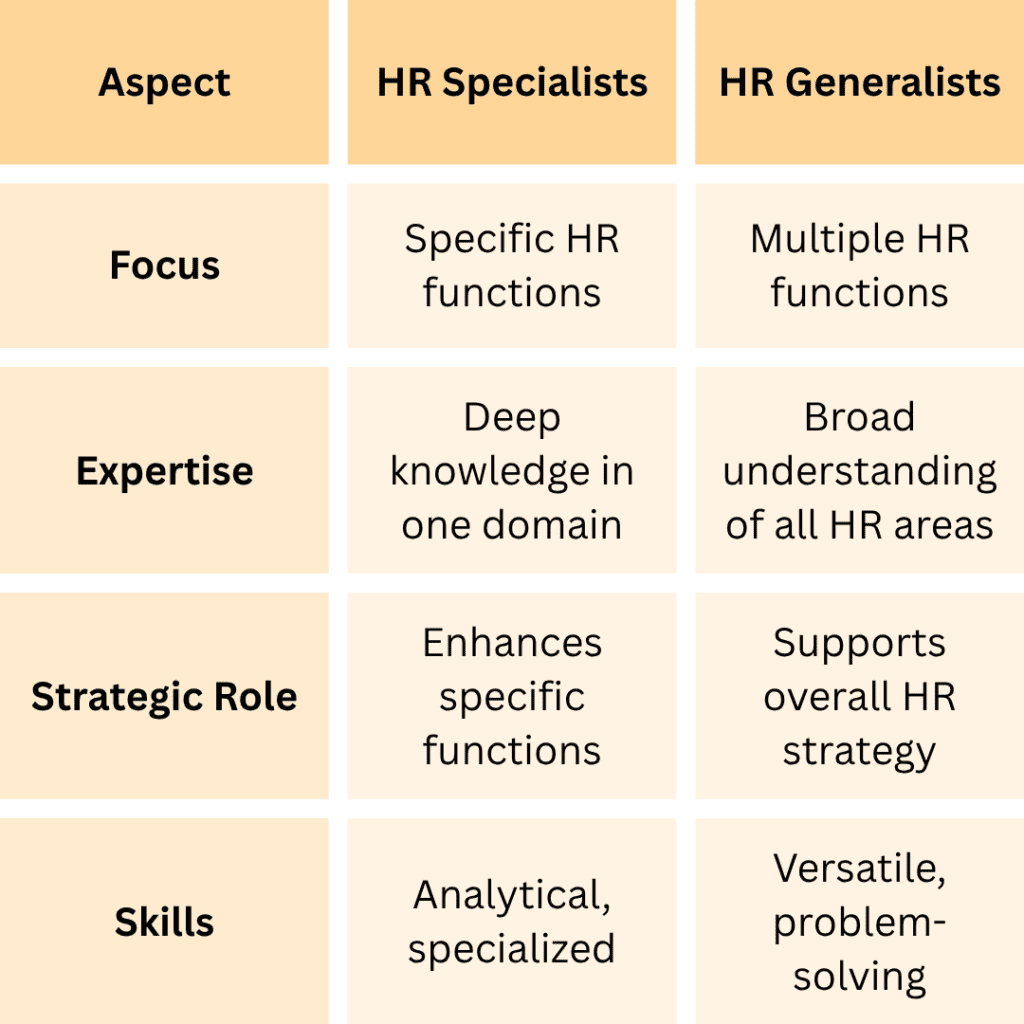
HR roles can be broadly classified into two categories: HR Specialists and HR Generalists. While HR specialists focus on specific functions, HR generalists handle a variety of tasks across the HR spectrum.
- HR Specialists: These professionals are experts in particular areas of HR, such as recruitment, employee relations, compensation, and training. They bring in-depth knowledge and strategic support to their specialized field.
- HR Generalists: Generalists manage a wide range of HR functions, including hiring, employee engagement, performance management, and compliance. They ensure the smooth running of day-to-day HR operations and help implement HR policies.
Difference between HR Specialists vs. HR Generalists

What are the Emerging Trends in HR Roles and Responsibilities?
The field of HR is constantly evolving to meet changing business needs and workforce dynamics. Emerging trends include:
- HR Analytics and Data Science: Using data-driven insights for workforce planning, employee engagement, and performance management.
- HR Technology and Automation: Implementing HR software solutions for recruitment, onboarding, payroll, and employee engagement.
- Employee Experience Managers: Focusing on enhancing the employee journey, from recruitment to retention, to boost productivity and satisfaction.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Specialists: Promoting inclusive workplace practices and ensuring equal opportunities for all employees.
- Change Management Consultants: Assisting organizations in navigating digital transformation, mergers, and restructuring.
As organizations adapt to remote work, digitalization, and changing employee expectations, the demand for specialized HR roles is increasing. Companies must stay updated with these emerging trends to build agile and future-ready HR teams.
Best Practices in Human Resources Management
Effective Human Resources Management (HRM) helps companies improve employee engagement, productivity, and overall success. By following best practices, HR teams can align their strategies with business goals and adapt to changing workforce needs.
Strategic HR Practices:
-
Workforce planning & talent acquisition
-
Employee engagement & retention programs
-
Performance management & career development
-
Diversity and inclusion initiatives
-
HR analytics for data-driven decisions
HR Compliance & Ethics:
-
Ensure legal adherence and fair treatment
-
Promote transparency and ethical practices
-
Protect whistleblowers and create safe reporting mechanisms
Future-Ready HR Strategies:
-
Digital transformation & HR technology adoption
-
Agile HR practices
-
Focus on employee well-being & experience
-
Leadership development & succession planning
-
Sustainability & Corporate Social Responsibility initiatives
What are the HR Transformation Strategies for Future Readiness?
To succeed in a rapidly changing business world, HR departments need to adopt new strategies. Key transformation strategies can include:
- Digital Transformation and HR Technology: Using modern HR tools, like AI-driven recruitment, HR analytics, and cloud-based systems, makes HR processes faster and more efficient.
- Agile HR Practices: Agile HR focuses on being flexible, working together, and adapting quickly to changes. This approach helps companies respond to new business needs and employee expectations.
- Employee Experience and Well-being: Supporting employees’ well-being, work-life balance, and mental health leads to happier, more productive teams.
- Leadership Development and Succession Planning: Training future leaders through mentorship and development programs ensures the company has strong leaders for long-term success.
- Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Including CSR and sustainability in HR practices improves the company’s brand image and keeps employees engaged.
Human Resource Management (HRM) is crucial for managing people and aligning their roles with organizational goals to enhance productivity and employee satisfaction. It includes Strategic, Operational, and Administrative HRM, each focusing on different aspects of workforce management. Key areas involve HR planning and development, HR policies and compliance, training and development, and operations and metrics, all supported by HR analytics and automation. HR outsourcing and consulting offer cost efficiency and strategic growth. The blog also distinguishes HR Specialists, who focus on specific areas, from HR Generalists, who manage end-to-end HR functions. Emerging trends like HR analytics, automation, and DEI specialists are shaping the future of HR. Best practices in strategic HRM, compliance, ethics, and transformation strategies help companies stay competitive and future-ready.