- About us
- Outsourcing
- Strategic Finance
- Compliance & Tax
- Automation
- Group Companies
- Resources
- Career
Automation is the use of technology to perform tasks or processes with minimal human intervention. It originated in industrial settings where machines were designed to replicate repetitive manual labor, think robotic arms on assembly lines or conveyor systems in factories. But today, automation has expanded far beyond manufacturing. It powers everything from smart home devices to AI-driven software that handles emails, data entry, and even customer service chats.
At its core, automation aims to increase efficiency, accuracy, and speed by reducing the reliance on manual input. Whether it’s controlling machinery with pre-set instructions or using algorithms to manage digital workflows, automation helps systems run smoothly and consistently.
In an increasingly digital world, automation is no longer optional; it’s essential. As industries evolve, understanding the foundations of automation helps individuals and businesses harness its full potential across sectors.
Business automation is the process of using technology to manage repetitive tasks, allowing companies to streamline workflows and focus on strategic work. It encompasses tools from simple workflow automation software to advanced platforms with AI. For example, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software “bots” to mimic human actions copying data, filling forms or moving files across applications. These business process automation tools help organizations run workflows with minimal human intervention, freeing teams to innovate instead of getting bogged down in paperwork. Businesses of all sizes use automation strategies to stay competitive by accelerating processes and supporting growth.
Industrial automation uses robots and computerized systems to perform manufacturing tasks once handled by people. On factory floors, robot arms assemble, weld or inspect parts nonstop with high precision. For example, automotive plants use robotic welders and painters, speeding production and reducing defects. These systems can run 24/7 with minimal supervision, making processes more efficient and cost-effective.
Automation provides many clear business benefits. It increases productivity and consistency while reducing human error and operating costs. By centralizing workflows on a single platform, companies gain visibility into every process step, improving compliance and decision-making. Staff no longer waste time on repetitive chores; freed-up employees can focus on innovation. In fact, research shows that when workers save time through automation, they typically invest it in new activities. Companies often see ROI quickly for example, marketing automation can deliver roughly five times the investment For example, one global insurer automated its finance closing process and saved roughly $40,000 per quarter. These gains from cost savings to faster time-to-market show why automation is strategic for businesses today.
Automation is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Depending on the industry and function, it can take various forms from machines operating on factory floors to AI software streamlining office workflows. Let’s explore the major categories of automation and how they’re shaping modern industries.
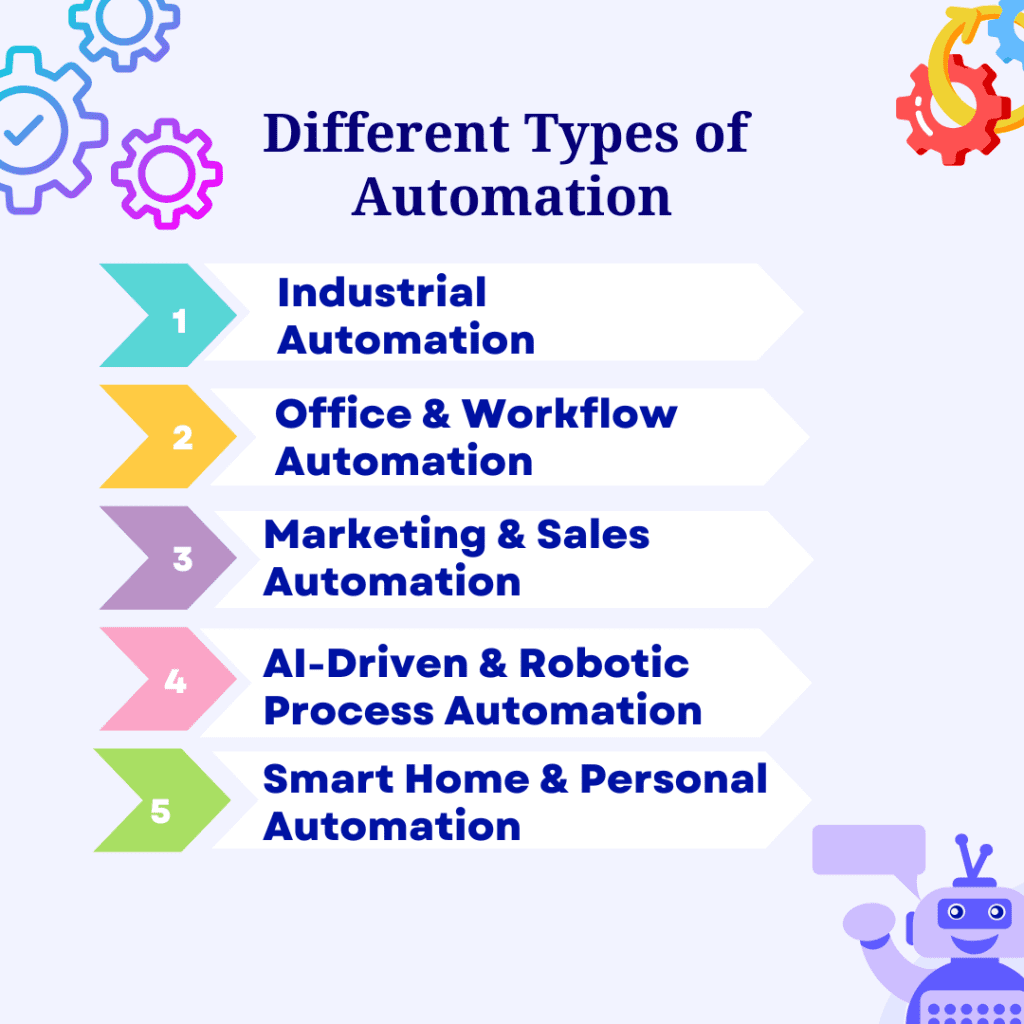
Industrial automation refers to the use of control systems like PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers), SCADA, and robotics to manage machinery, processes, and production lines.
For example, automotive manufacturers use robotic arms and conveyor belts that operate in sync to assemble vehicles with unmatched precision. PLC systems monitor and control temperature, pressure, and speed to ensure smooth production without human error.
Example: A car manufacturer using RPA (Robotic Process Automation) for inventory tracking and PLC systems for mechanical operations achieves real-time visibility and zero downtime.
In offices, automation eliminates repetitive administrative tasks like data entry, approvals, or reporting. Tools like Microsoft Power Automate and Zapier allow businesses to connect apps, automate email follow-ups, and generate reports automatically.
Example: A finance team using workflow automation tools can automatically collect invoices from emails, match them with purchase orders, and send them for approval all without manual effort.
Benefits:
Marketing automation involves using AI-driven automation tools to personalize campaigns, manage leads, and analyze engagement metrics. Platforms such as HubSpot or Mailchimp can automate email campaigns, social media posts, and customer follow-ups.
Similarly, sales automation tools within a CRM with automation system help sales teams track leads, schedule reminders, and manage pipelines automatically.
Example: A real estate company using sales automation tools can send personalized property recommendations to potential buyers and automatically update CRM records after every client interaction.
The rise of AI-driven automation and RPA software has taken efficiency to a new level. These systems mimic human actions like reading invoices, understanding natural language, or analyzing data patterns but do it faster and more accurately.
Example: In healthcare, AI automation systems analyze patient data to predict diagnoses, while RPA tools handle appointment scheduling and billing tasks.
Automation isn’t limited to industries or offices. Smart home automation allows individuals to control lighting, security, temperature, and entertainment systems with voice commands or mobile apps.
Example: Using smart home assistants like Alexa or Google Home, users can automate lighting schedules, receive energy usage insights, or even trigger safety alerts in case of anomalies.
In essence, automation touches nearly every aspect of modern life from factories to living rooms. Each form of automation aims to make processes faster, smarter, and more reliable, ultimately empowering humans to focus on creativity, innovation, and decision-making.
Automation is no longer a futuristic concept it’s a practical advantage that empowers industries, businesses, and individuals to operate faster, safer, and more efficiently. Whether it’s an automated assembly line or a digital workflow, the benefits of automation are far-reaching.
One of the most significant benefits of automation is accuracy. Machines and software systems perform repetitive tasks without fatigue, reducing human error. In manufacturing, industrial automation systems ensure consistent product quality and production precision.
In corporate environments, business process automation tools automatically capture and process data across platforms from invoices to customer information with minimal errors.
Example:
A pharmaceutical manufacturer using SCADA systems and PLC programmable logic controllers can maintain strict quality standards by monitoring every production stage in real-time. This ensures that no faulty batch passes undetected.
Automation helps organizations lower their operational costs by minimizing manual labor, reducing downtime, and improving utilization of existing resources.
Manufacturers can use RPA (Robotic Process Automation) to streamline documentation, compliance checks, and machine scheduling all of which reduce overhead costs.
Example:
A textile manufacturer integrated open source RPA tools to automate inventory management, saving hundreds of labor hours each month and reducing stock mismatches by 90%.
Automation tools equipped with AI-driven analytics provide decision-makers with real-time insights. For instance, an automated dashboard in a workflow management system can analyze project progress, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements instantly.
Example:
In the finance sector, AI-driven test automation validates large volumes of data within seconds, helping CFOs make timely decisions about cash flow and risk management.
Automation isn’t only about efficiency it’s also a key to maintaining regulatory compliance. Businesses today rely on RPA software to maintain audit trails, ensure accurate reporting, and meet data privacy standards.
Automated systems can detect anomalies, track document history, and ensure that every record complies with standards such as ISO, GDPR, or local tax regulations.
Example:
An accounting firm uses Power Automate RPA to standardize tax filing processes and automatically validate entries for compliance, reducing audit risks.
Before investing in automation, every business must first identify repetitive and rule-based tasks that consume time and resources. These could include invoice processing, inventory tracking, email follow-ups, or compliance audits.
Pro Tip:
Start small use workflow automation tools or CRM with automation for pilot projects. Once results are measurable, scale automation across departments.
Example:
A mid-sized manufacturer began with automating quality checks using QA automation engineers, then expanded automation to supply-chain tracking using industrial automation systems.
Selecting the right technology is critical for success. Popular tools include:
Tip: Evaluate tools based on scalability, integration capability, and security compliance.
Automation works best when employees are trained and engaged. Rather than replacing human roles, automation augments human potential.
Organizations should encourage teams to collaborate with digital systems and leverage insights from AI-driven automation.
Example:
A retail chain trained its sales staff to use sales automation tools that automatically update leads and generate sales reports improving customer follow-ups and conversions by 40%.
Automation is not a one-time implementation, it’s an ongoing improvement process. Regular monitoring ensures that automated workflows remain relevant and efficient as business goals evolve.
Using open-source RPA tools and workflow management systems, organizations can easily test new processes, collect feedback, and scale with confidence.
Example:
A logistics company tested AI-based routing via business process automation tools, reducing delivery time by 25% while cutting fuel costs.
By 2025, automation is evolving from simple rule-based systems to AI-powered ecosystems capable of learning, predicting, and self-optimizing.
AI automation and machine learning-driven processes will dominate industries from smart home automation to predictive business intelligence.
Future-ready businesses are already integrating AI-driven automation into their core operations to stay competitive, compliant, and connected.
Automation refers to using technology, software, or machines to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. In 2025, it’s vital because it drives efficiency, reduces costs, and supports digital transformation across industries.
The key types include industrial automation, business process automation, RPA (Robotic Process Automation), AI-driven automation, and marketing automation tools each designed for different operational needs.
Small businesses can use affordable tools like Zapier or Power Automate RPA to streamline billing, email marketing, HR, and customer support improving productivity and reducing manual errors.
Popular tools include UiPath, Microsoft Power Automate, TOSCA, SCADA, and AI-driven test automation platforms that help organizations integrate, monitor, and optimize workflows.
Automation won’t replace humans entirely it will replace repetitive tasks. Humans will move toward roles that require strategy, creativity, and problem-solving supported by automation for execution.
Begin by identifying repetitive workflows, choosing the right automation software, training your team, and gradually expanding the system after evaluating ROI and efficiency improvements.
Automation is redefining how businesses, manufacturers, and individuals work, plan, and grow.
From industrial automation that powers production lines to marketing automation that personalizes customer engagement, the potential is limitless.
Organizations that embrace automation today are not just saving time, they’re investing in precision, scalability, and innovation.
As we move into an AI-first era, automation isn’t optional, it’s the foundation of smarter, more agile enterprises.
In short: Automate intelligently. Grow sustainably. Compete globally.
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.